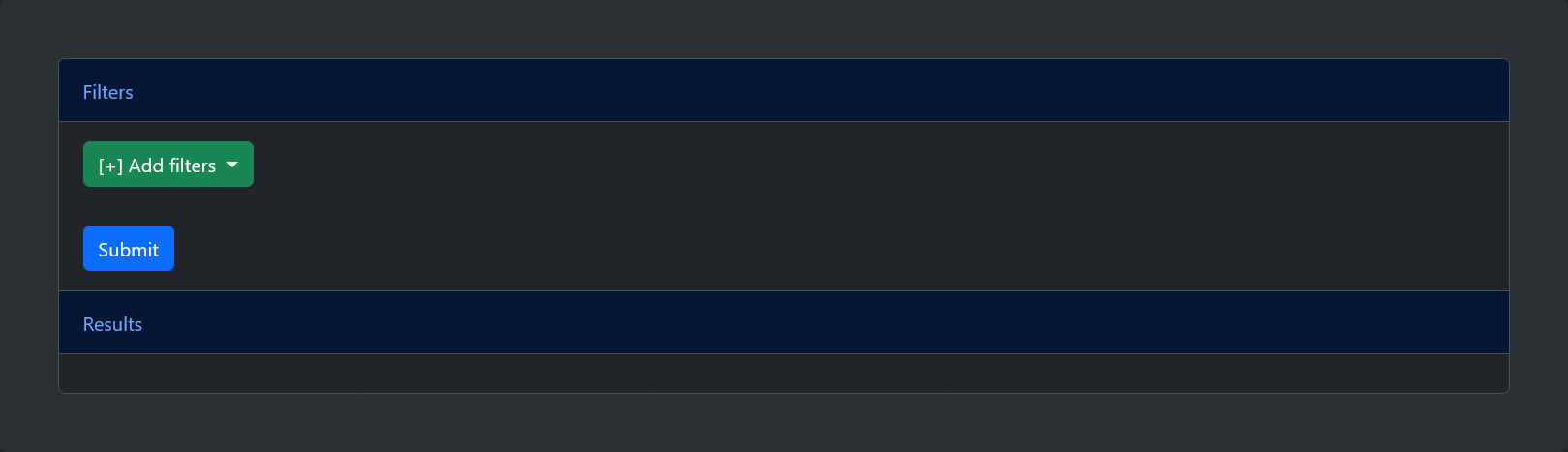
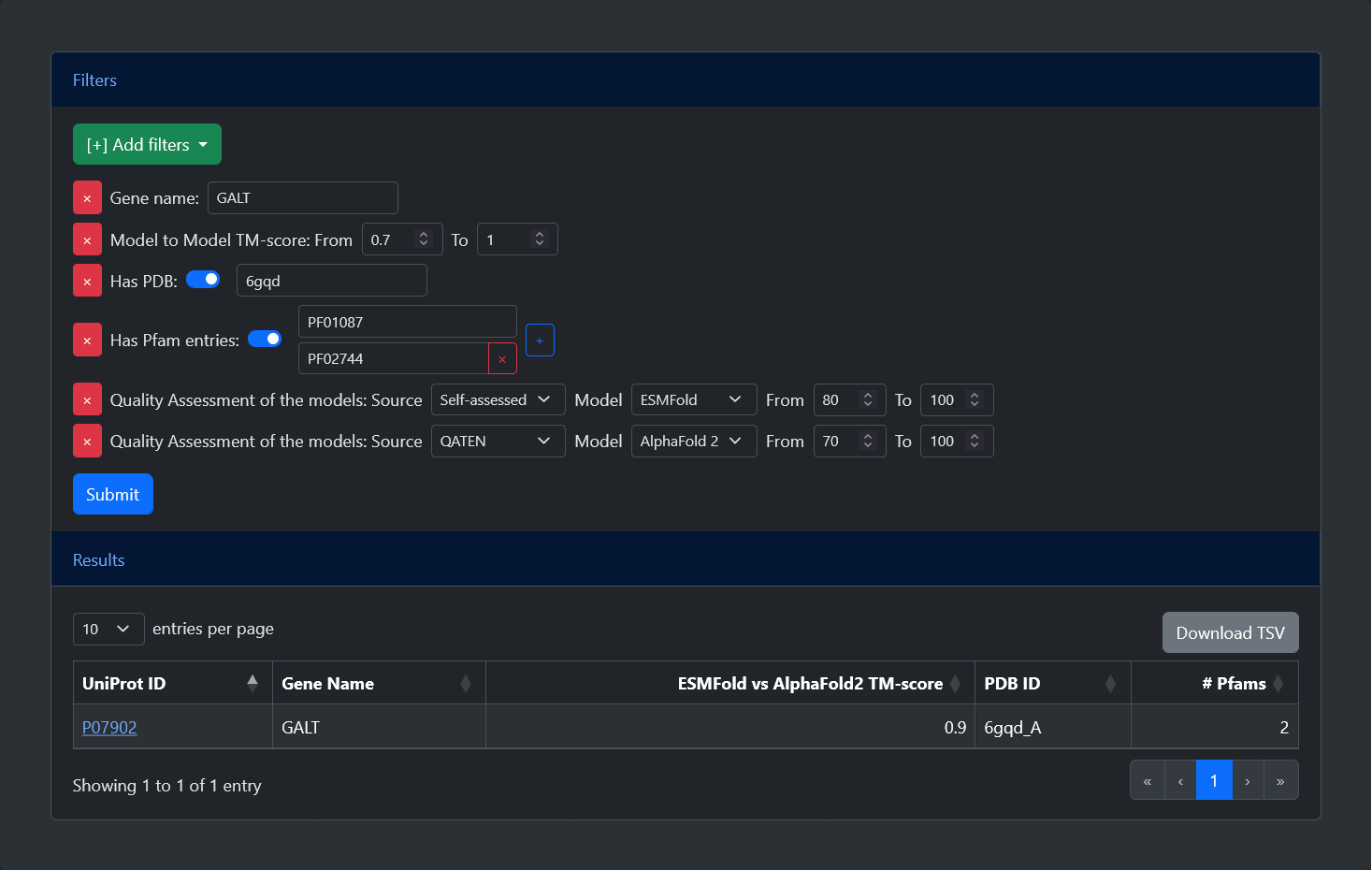
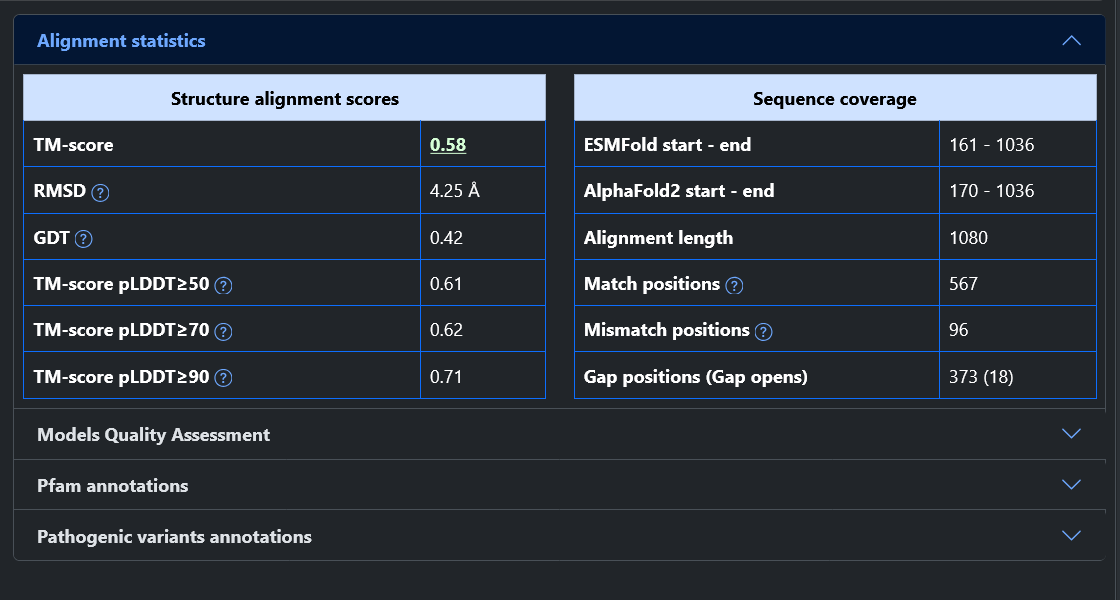
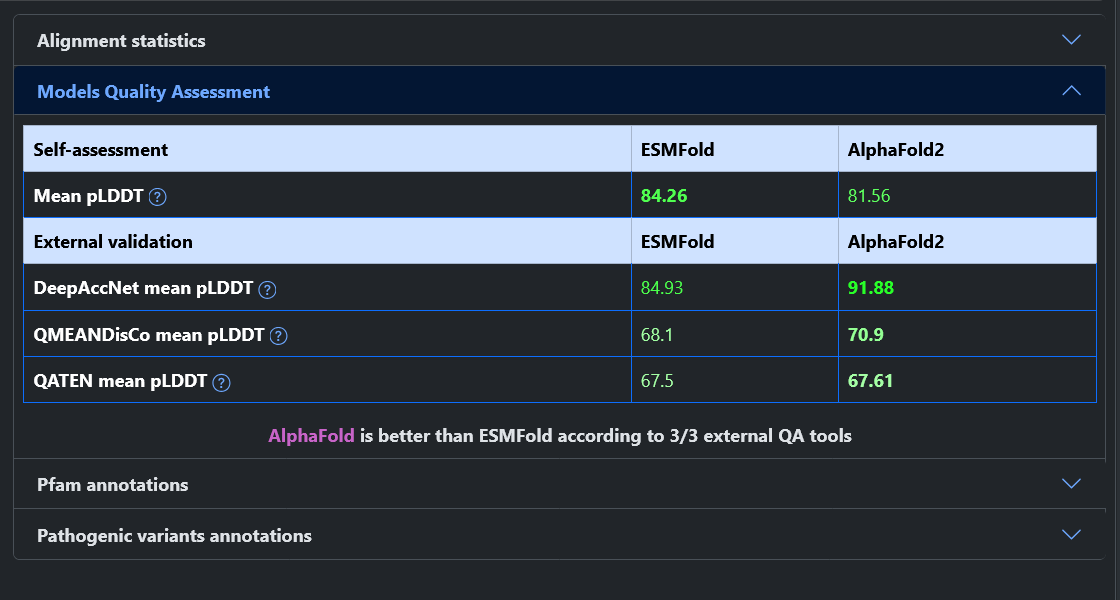
From the home page of the web server, it is possible to query the model database in two ways:
-
UniProt accession: the accession is searched against the database and, if present, all data for the entry are shown. Otherwise, an error message is displayed prompting the user to go back to the home page.
The same search functionality is available also outside the home page, through the “Quick search” field in the navigation bar at the top of each page.
-
FASTA sequence: the protein is aligned against all the sequences present in our database using BLAST. Depending on the results, a list of at most 10 entries is displayed.
-
If a perfect match is found, only the corresponding entry will be displayed.
-
If at least one significant match is found, the best significant hits will be displayed. We consider a hit to be significant if it has an e-value lower than 0.001 and a sequence identity greater than 50% over a coverage greater than 70%.
-
If no significant match is found, the best hits will be displayed alongside a warning message.
-
If no hit is found, an error message is displayed prompting the user to go back to the home page.